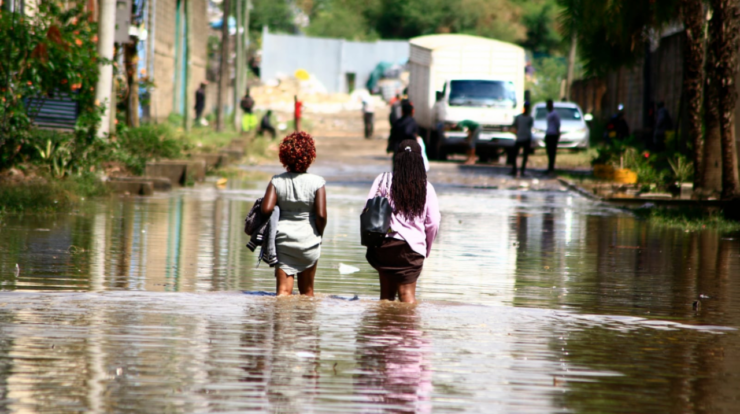
Kenya nairobi flooding – Kenya’s capital city, Nairobi, has become a victim of relentless flooding, leaving its mark on the city’s infrastructure, economy, and the lives of its people. Understanding the causes, consequences, and efforts to combat this ongoing crisis is crucial for charting a path towards a more resilient future.
The incessant downpours have wreaked havoc on Nairobi’s infrastructure, disrupting transportation, damaging buildings, and overwhelming drainage systems. The economic toll is equally concerning, with businesses suffering losses and livelihoods being threatened.
Flooding in Nairobi, Kenya
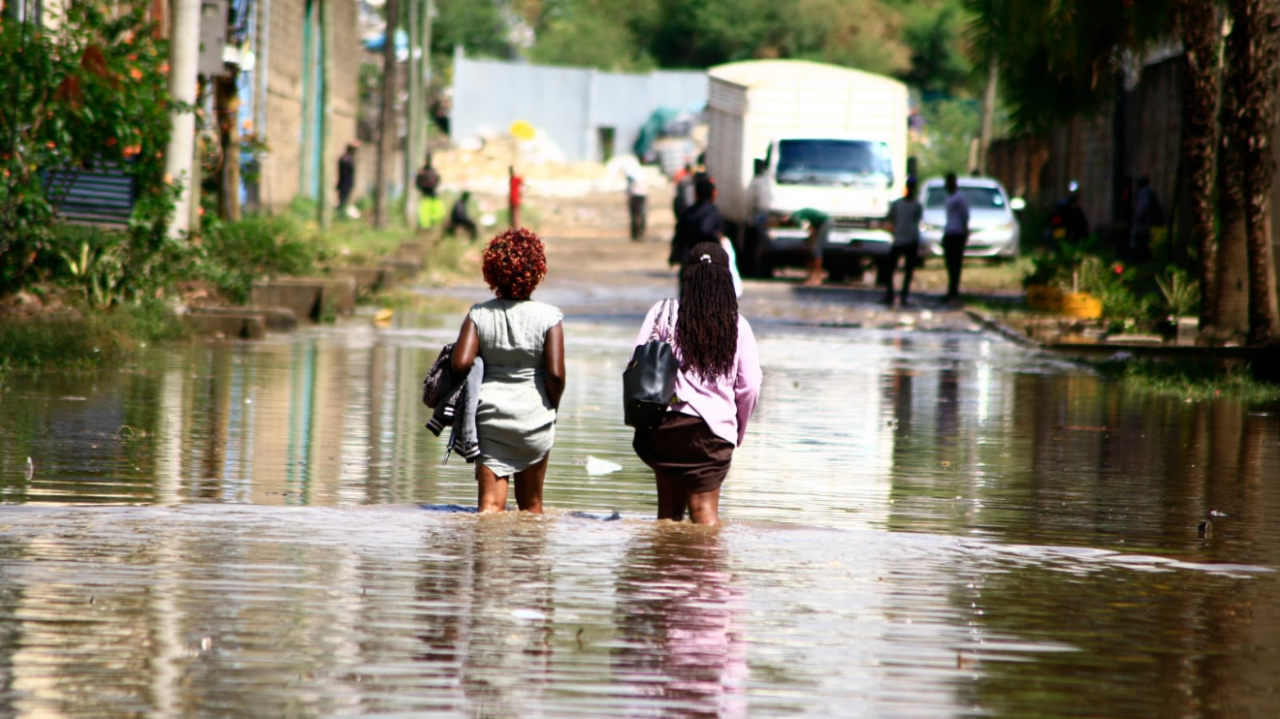

Flooding has been a recurring issue in Nairobi, Kenya, posing significant challenges to the city’s infrastructure, economy, and population. The problem has been attributed to a combination of factors, including heavy rainfall, poor drainage systems, and inadequate urban planning.
Causes and Contributing Factors
- Heavy rainfall:Nairobi experiences intense rainfall during the rainy seasons, particularly from March to May and October to December. The city’s location in a valley surrounded by hills contributes to the accumulation of rainwater.
- Poor drainage systems:Nairobi’s drainage infrastructure is inadequate to handle the volume of rainfall. Many drainage channels are clogged with debris and solid waste, impeding the flow of water.
- Inadequate urban planning:The city’s rapid urbanization has led to the construction of informal settlements in flood-prone areas. Poor land use planning and lack of proper drainage systems in these settlements exacerbate the flooding problem.
Impact of Flooding
- Infrastructure damage:Flooding can damage roads, bridges, buildings, and other infrastructure, disrupting transportation, communication, and essential services.
- Economic losses:Flooding can cause business disruptions, damage to property, and loss of income, particularly for small businesses and low-income communities.
- Health risks:Stagnant water after flooding can create breeding grounds for mosquitoes, increasing the risk of malaria and other waterborne diseases.
- Social displacement:Severe flooding can displace people from their homes, leading to temporary or permanent relocation.
Government and Municipal Response to Flooding
The Kenyan government and Nairobi City Council have implemented several measures to address flooding, including:
Policies and Regulations
- Nairobi Integrated Urban Development Master Plan (NIUUDP):This plan Artikels a comprehensive strategy for flood management, including the construction of new drainage systems, flood retention ponds, and improved land use planning.
- Environmental Management and Coordination Act (EMCA):This act provides a legal framework for environmental protection, including the regulation of land use and development in flood-prone areas.
Infrastructure Projects
- Nairobi Sewerage and Drainage Improvement Project:This project involves the construction of new and improved drainage systems in various parts of the city, including the installation of underground pipes, culverts, and floodgates.
- Ngong River Basin Rehabilitation Project:This project aims to restore the Ngong River, a major tributary that flows through Nairobi, by removing debris and improving its flow capacity.
Evaluation and Challenges, Kenya nairobi flooding
While these measures have helped to mitigate flooding to some extent, challenges remain. The implementation of the NIUUDP has been slow, and enforcement of environmental regulations has been inconsistent. Inadequate funding and technical capacity have also hindered the effectiveness of flood management efforts.
Community Resilience and Adaptation
Local communities in Nairobi have played a crucial role in adapting to and coping with flooding. Community-led initiatives include:
Flood Preparedness and Response
- Early warning systems:Community groups have established early warning systems to alert residents to impending floods, allowing them to evacuate or take precautionary measures.
- Community flood brigades:These volunteer groups assist in flood response efforts, providing support to affected residents, clearing debris, and distributing relief supplies.
Long-Term Adaptation Strategies
- Urban farming and green infrastructure:Community gardens and green spaces can help absorb rainwater and reduce runoff, mitigating the impact of flooding.
- Improved housing design:Community members have adopted flood-resistant building techniques, such as elevating homes and installing flood barriers, to protect their properties.
International Collaboration and Support
Several international organizations have provided assistance to Nairobi in its flood management efforts, including:
Organizations and Partnerships
- World Bank:The World Bank has provided funding and technical support for the Nairobi Sewerage and Drainage Improvement Project.
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP):UNDP has supported community-based flood adaptation projects, including the establishment of early warning systems and flood brigades.
Types of Assistance
- Funding:International organizations provide financial assistance for flood mitigation projects and disaster relief efforts.
- Technical expertise:Experts from international organizations share knowledge and best practices in flood management, helping Nairobi to develop and implement effective strategies.
- Capacity building:International organizations provide training and capacity building programs for local authorities and community groups, empowering them to manage flooding more effectively.
Future Challenges and Recommendations
Despite ongoing efforts, Nairobi faces future challenges related to flooding, particularly considering the impacts of climate change and urbanization.
Climate Change and Urbanization
- Increased rainfall intensity:Climate change is projected to lead to more frequent and intense rainfall events, exacerbating flooding in Nairobi.
- Urban expansion:The continued growth of Nairobi’s population and urban areas will increase the demand for land, potentially leading to the development of new settlements in flood-prone locations.
Recommendations
- Strengthening early warning systems:Investing in early warning systems and public education campaigns to enhance flood preparedness.
- Improving drainage infrastructure:Expanding and maintaining drainage systems to handle the increased volume of rainfall and reduce waterlogging.
- Promoting sustainable urban planning:Implementing land use regulations and urban planning strategies that prioritize flood resilience and minimize development in flood-prone areas.
- Enhancing community engagement:Fostering collaboration between government agencies, community groups, and NGOs to develop and implement community-led flood management initiatives.
Final Wrap-Up
As Nairobi navigates the challenges posed by flooding, a multifaceted approach is required. Continued investment in infrastructure, community-led initiatives, and international collaboration are essential for building a more resilient city. By embracing innovation, fostering community engagement, and leveraging global expertise, Nairobi can emerge from this crisis stronger and better equipped to withstand future floods.
FAQs: Kenya Nairobi Flooding
What are the primary causes of flooding in Nairobi?
Nairobi’s flooding is primarily attributed to heavy rainfall, poor drainage systems, and unplanned urbanization.
How has flooding impacted Nairobi’s economy?
Flooding has caused significant economic losses, disrupting businesses, damaging infrastructure, and affecting livelihoods.
What role do local communities play in flood management?
Local communities play a crucial role in flood preparedness, response, and recovery through early warning systems, community-led initiatives, and raising awareness.